During the course of the disease in question, the proper shape and elasticity of the intervertebral discs is lost: their gradual deformation occurs. The distance between the vertebrae decreases, leading to pinched nerves and pain. Among all parts of the spine, the lumbosacral is the most susceptible to these pathological changes.
Causes and signs of lumbar osteochondrosis - how does the disease manifest itself?
The disease in question occurs due to improper distribution of the load on the spine. This is the main reason for diagnosing lumbar osteochondrosis. Many factors can cause the appearance and development of this disease.
- Passive lifestyle. This includes people who lead a predominantly sedentary lifestyle. In a sitting position, the ligaments relax, which increases the load on the lumbar spine.
- Inflammatory phenomena localized in the joints of the spine.
- Errors in the functioning of the endocrine system, hormonal imbalance.
- Serious infectious diseases affecting bones and joints (tuberculosis, osteomyelitis).
- Gastrointestinal and cardiac disorders.
- Lifestyle related to heavy physical work (loaders, weight lifters, construction workers).
- Uneven posture, incorrect gait.
- Poor cartilage tissue density (hereditary factor).
- Congenital pathologies related to the spine/skeletal structure. Differences in the functioning of the locomotor system.
- Obesity.
- Unbalanced work and rest system.
- Circle. After crossing the 50-year threshold in humans, the intervertebral discs become less flexible and inactive.
- Chemical poisoning.
- Crow's feet. With the proper structure of the foot, the load is absorbed while walking. In the case of flat feet, the intervertebral discs receive maximum load, which leads to their deformation and destruction.
- Back injury.
The signs of the disease in question can be divided into three groups. Reflex signals (pain). They have many manifestations:
- Lumbago. It develops as a result of sudden movement (high jump, running, coughing). This pain is paroxysmal (lumbago). During this attack, the patient tilts his trunk forward and remains in this position for a certain time: attempts to straighten up cause a new wave of pain. Lumbago occurs as a result of pinching of nerve roots.
- Lumbodynia. Pain in the lumbar region is increasing in nature. In the beginning, the patient feels some discomfort, which can turn into severe, regular pain. Lumbodynia can be caused by a sedentary lifestyle and excessive physical activity. Lumbodynia can develop against the background of lumbago.
- Sciatica. The sensation of pain spreads along the sciatic nerve. The main place is the lower limbs. This phenomenon occurs when the nerve roots of the spinal cord are compressed. If the motor fibers are involved in the destructive process, the patient experiences muscle spasms and muscle weakness. Ignoring these symptoms can lead to muscle atrophy in the future.

Radicular syndrome. It is characterized by the following manifestations:
- the skin of the legs sometimes loses its sensitivity;
- the patient complains of pain in the lumbar region;
- disturbances occur in the sweating system.
Radicular-vascular signs. They occur against the background of compression of blood vessels. The following complaints occur from the patient:
- warm/cold sensation in the lower limbs;
- slight tingling / increasing pain in the leg;
- swelling (if the veins are compressed).
Lack of proper treatment can cause spinal bleeding, which can lead to partial/total paralysis of the lower limbs and serious dysfunction of the pelvic organs. Lumbar osteochondrosis negatively affects the structure of the vertebrae: they can shift over time. This violation can provoke a number of negative phenomena.
- Functional disorders of the internal organs and the urinary system.
- Frequent fatigue.
- Weakness.
- Irritability.
Symptoms of lumbosacral osteochondrosis depending on the degree - how is the disease diagnosed?
Based on the set and strength of the clinical symptoms, the disease in question is divided into several stages. The first is initial, the second is mild, and the third is severe.
1st degree lumbar osteochondrosis.
The main symptoms are characterized by:
- Lumbago (lumbago), which occurs due to the rupture of the (intervertebral) disc capsule.
- Swelling of tissues.
- Muscle cramp.
- Regular pain.
In the case of grade 1 lumbar osteochondrosis, the patient may experience additional symptoms caused by compression of blood vessels and nerve roots.
- Imitation of disorders related to the functioning of the kidneys and gastrointestinal tract.
- Intermittent abdominal pain that occurs against the background of spasm of the abdominal muscles.
Lumbar osteochondrosis 2nd degree.
This degree of lumbar osteochondrosis is also characterized by the following manifestations:
- Regular pain (lumbodynia). The place of pain of varying intensity is the lower back.
- Non-standard mobility in the joints of the spine. A tight bandage on the lower back can improve the patient's general condition and reduce pain for a short time.
- Internal organ dysfunction (not always). In some cases, patients with lumbar osteochondrosis may experience bronchial asthma and biliary/urinary tract dysfunction.
- Pain in the lower limbs, which goes in the direction of the sciatic nerve.
3rd degree lumbar osteochondrosis.
At this stage of the disease, surgical treatment is necessary, otherwise paralysis and death may occur. The 3rd degree of lumbar osteochondrosis has its own characteristics.
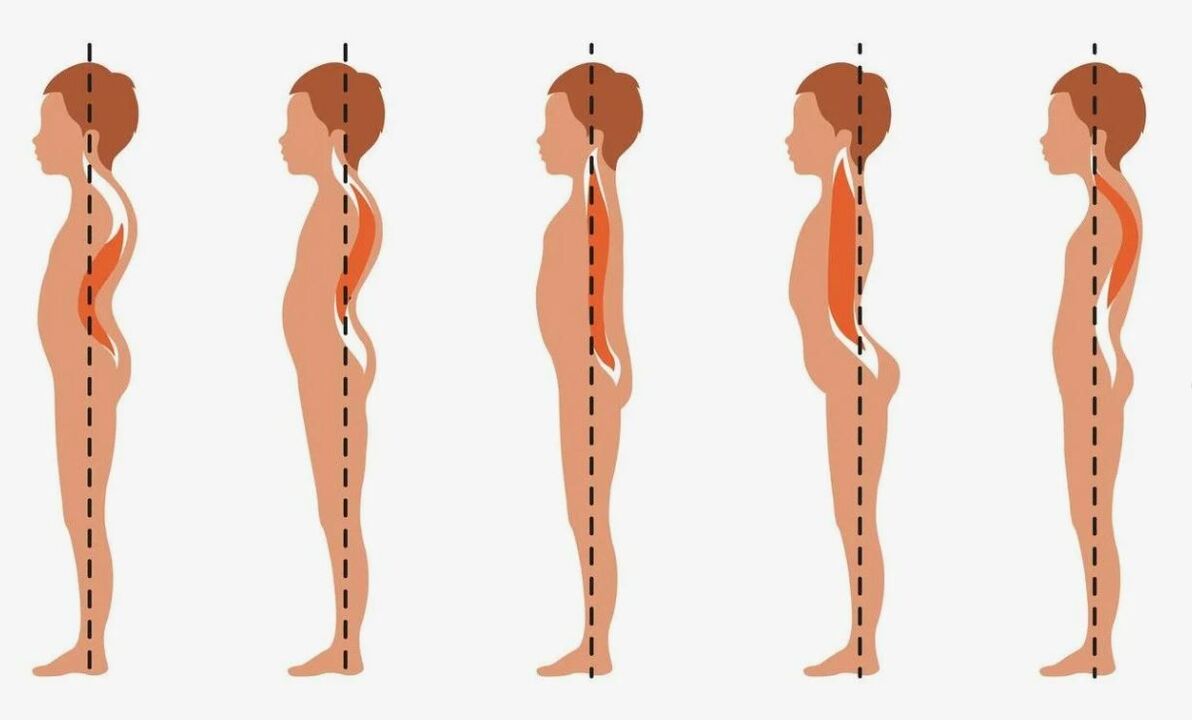
- Spinal deformities: curvature to the right/left (scoliosis); forward bending (lordosis), curvature of the lumbar spine (kyphosis).
- Constant, severe, acute pain that can be felt even with the slightest physical activity (changing position, coughing, sneezing).
- Swelling of muscle tissue and ligaments.
- Periodic/regular numbness in the lower part of the body (lower back, legs, feet).
- Dysfunctions of the urogenital system.
Treatment methods of lumbar osteochondrosis
The choice of treatment tactics for the disease in question depends on the degree of osteochondrosis, the presence of additional diseases, the general condition of the patient and other factors that the attending physician must take into account.
There are two important aspects that guide all doctors when prescribing treatment.
- In order to eliminate osteochondrosis of the lumbar region, an integrated approach is needed.
- Treatment measures (intensity, duration) are determined by the degree of neglect of the pathology in question.
Drug treatment of lumbosacral osteochondrosis - effective drugs
Every year, scientists develop new drugs that help alleviate the symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis. The list of medicines below is not standard and may change. Today, however, doctors often use certain drugs to combat the manifestations of the disease.
- Chondroprotectors. They stop the destructive processes that take place in the cartilage tissues of the spine in the initial stages of the disease.
- Anti-inflammatory (non-steroidal) drugs. It is used to treat 2nd degree lumbosacral osteochondrosis. This group of drugs can be used in the form of injections (intramuscular), tablets, ointments, rectal suppositories, capsules and solutions. In case of worsening of the disease, the patient can prescribe injections (16 mg/day)
- Muscle relaxants. Helps eliminate discomfort caused by increased muscle tone.
- vasodilators. It helps improve blood circulation, prevents stagnation, and minimizes the risk of infection in the body.
- Local anesthetics. In case of strong, constant pain, the anesthesiologist performs a blockade. Using a special needle, a solution is injected into the painful area. The pain goes away immediately and does not bother me for several weeks. Such a blockade should only be used in extreme cases: it has many negative consequences.
- Vitamin and mineral complexes. It is often prescribed to elderly patients to increase the strength of tendons and ligaments.
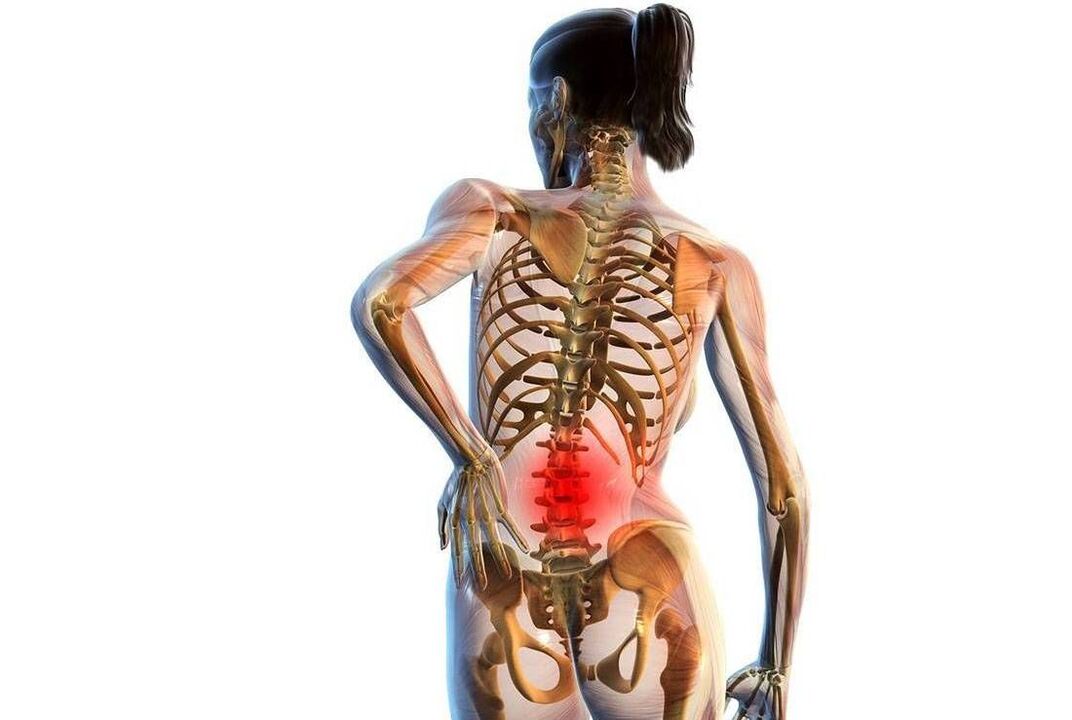
Massage for lumbar osteochondrosis of the lumbosacral region
This method of treatment will be useful in the subacute stage of the disease in question. Massage can eliminate pain, relieve muscle tension and stiffness.
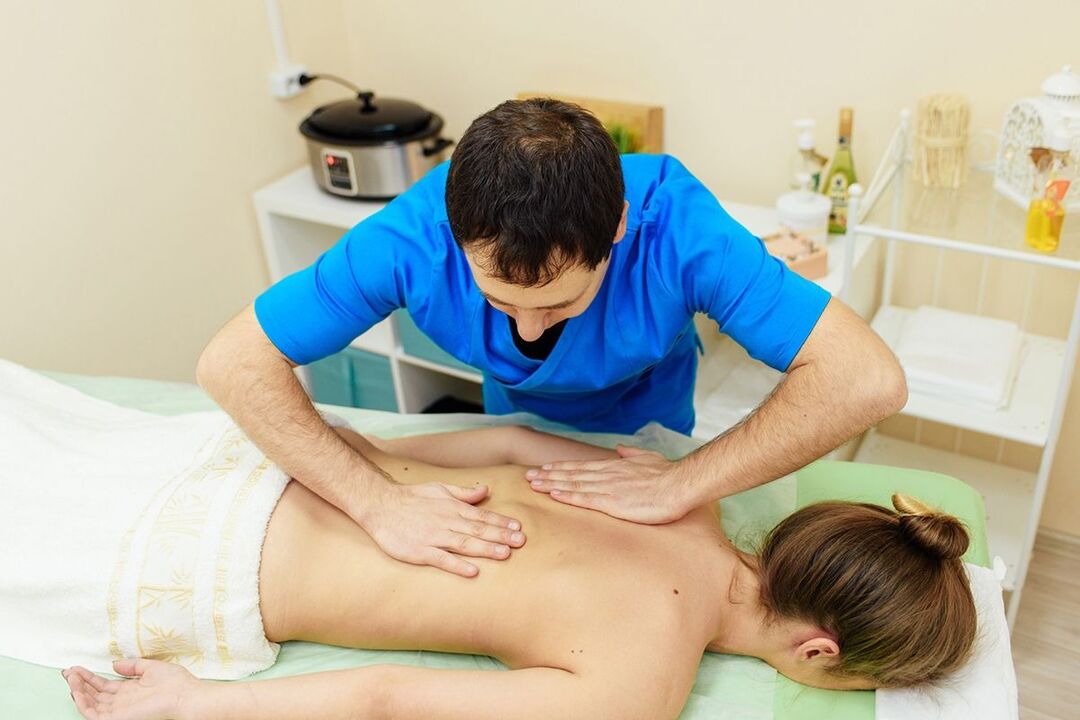
The massage must be performed in a healthy (not affected! ) area. During the procedure, the patient must be placed on a flat, hard couch on his stomach. Place a pillow/pillow under your belly. It is also necessary to ensure that the patient's legs are raised (45 degrees). The forehead must rest on a hard surface.
To perform the massage, it is better to use special products (oils, creams, body lotions) that have warming properties, or to perform the treatment immediately after thermal procedures (bath, sauna). Today, there are many massage techniques, let's highlight the main ones:
- To caress. There are several types of blows: hook-shaped, transverse flat, fan-shaped, ending with symmetrical blows in the area of the sternum muscles.
- Squeeze. It is performed in combination with stroking. This massage technique ensures that the muscles are stretched.
- Kneading.
- Shaking.
- Trituration. It is often used to improve the function of tendons, ligaments and joints.
- Point effect. Not all massage therapists can perform the procedure using the acupressure technique.
Therapeutic gymnastics or gymnastic therapy for lumbar osteochondrosis - a series of exercises for the lumbosacral spine on the video.
The entire complex of physical exercises used to diagnose lumbar osteochondrosis should help increase the mobility of the lumbar region.
Therapeutic gymnastics will not be effective if the exercises are performed occasionally. The main principle of exercise therapy is regularity. Continuous execution of a certain series of exercises helps to eliminate destructive processes in the intervertebral joints. In the presence of acute pain, exercise therapy is prohibited. In case of severe pain, doctors recommend bed rest and wearing a special corset. When the pain subsides, you can try therapeutic exercises.
Physiotherapy of lumbar osteochondrosis
This conservative treatment method is one of the most effective. However, to achieve the desired result, you need to spend a lot of time. The simultaneous use of several types of physiotherapy helps speed up recovery. This method of treatment has many contraindications that cannot be ignored. Physiotherapy is often prescribed for children, pregnant women, nursing mothers and elderly patients.
The use of physiotherapy is prohibited in the following cases:
- Cancer;
- acute stages of osteochondrosis;
- severe disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system;
- injury in the area where physiotherapy is to be performed.
Nowadays, many physiotherapy procedures have become popular in the treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis.
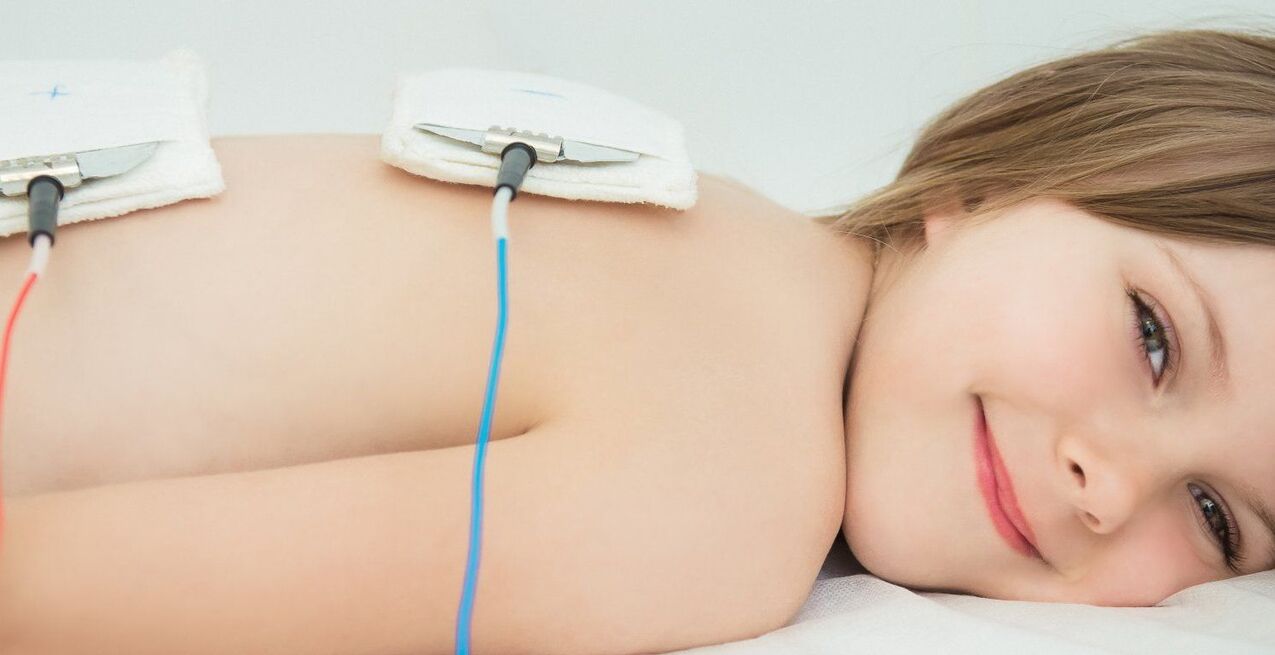
- Ultraviolet radiation. The pathological area is exposed to heat, which helps to improve blood supply, eliminate spasms and eliminate pain.
- Magnetotherapy, electrophoresis. The application of the method involves applying a magnetic/electric field to the painful area of the spine. Through this effect, it is possible to start the body's metabolic processes, to eliminate (partially/completely) inflammatory phenomena, and to speed up healing.
- Laser therapy. The condition of the affected spinal roots improves significantly as a result of the helium-neon emitters applied to them.
- Balneotherapy. The main components of the physical procedure in question are medicinal mud and mineral waters.
- Detensor therapy (mechanical stretching of the spinal column). Relevant for severe back pain.
Folk remedies for lumbar osteochondrosis
This method of treatment involves the use of herbal ointments, rubs and poultices. Such remedies help reduce inflammation and eliminate pain. In the treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis, it is advisable to use folk remedies with caution: an allergic reaction may occur.
In the fight against the disease, rubbing and compresses are often used:
- Tincture of red pepper: for rubbing the painful areas of the lower back. To prepare the medicine, mix 1 tbsp. vodka (diluted medical alcohol), 20-25 gr. dry ground red pepper. These ingredients should be infused (stirring occasionally) for 5-7 days.
- Camphor and mustard: for daily rubbing before going to bed. To prepare the product, mix mustard powder (50 g), camphor alcohol (50 ml), medical alcohol (90-100 ml), beaten egg whites (3 pcs. ). After thorough mixing, you should get a liquid ointment.
- Honey and aloe: for poultice on the lower back (2 times a day). Honey (100 ml), diluted medical alcohol (150 ml), aloe juice (50 ml) should be used to prepare the product. Before use, this mixture should stand for 10-12 hours.
- Horseradish root and alcohol: to rub the affected part of the back. To prepare the product, mix horseradish root juice and medical alcohol in equal proportions. After rubbing, wrap the treated area.
- Garlic juice and pork fat (1: 2): to rub the painful areas of the lower back.
- Cabbage leaves peeled from thick veins: for poultice. Before application, the cabbage leaf must be immersed in hot water (no higher than 60 C). You can fix the sheet with bandage/gauze on the lower back. After changing the color of the letter, the procedure can be repeated.

Prevention of lumbar osteochondrosis
Prevention of the disease in question includes a whole series of measures.
Proper nutrition. The diet should be balanced and low in calories. It is not recommended to eat more than 6 times a day. Certain foods should predominate in the daily diet.
- Fish (sea).
- Vegetable fats (olive, linseed oil).
- Dairy products with minimal coloring and sugar content.
- Foods containing gelatin (jelly meat, jelly).
- Animal cartilage (can be used to prepare first courses).
- Fresh fruits and vegetables.
- Foliage.
- Mineral water.
Taking vitamin and mineral complexes (1-2 times a year) will be useful.
Active lifestyle
- Swimming.
- Daily walks.
- Gymnastic exercises (also suitable for pregnant women).
Performing simple physical exercises (15-20 minutes a day) to strengthen the back muscles.
Lumbar osteochondrosis can go from an acute stage to a chronic stage, and this means spending on massages, pain-relieving injections and warming ointments on an annual basis. If you do not treat all of this, the consequences can be very sad, even paralysis or death!